ADHD In Children: Symptoms & Treatment You Need to Know
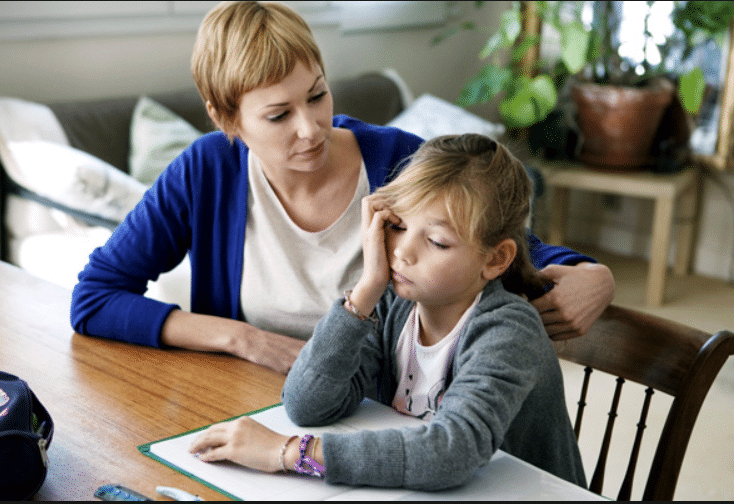
ADHD, or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, is among the most typical neurodevelopmental conditions; ADHD affects millions of children globally. Such kids may experience trouble focusing, sitting still, impulsive actions, and over-activity. While it can be routine for children 12 & Up to experience these habits, those diagnosed with ADHD have more consistent symptoms that can significantly disrupt their everyday life.
The main objective of this post is to equip you with necessary information about kids with ADHD. We shall discuss common indicators and symptoms as well as various kinds and current effective treatment approaches. When you are aware of what ADHD entails, you can foster a supportive atmosphere for such children. Mothers, fathers, educators and caretakers should collaborate in order to enable children diagnosed with ADHD to proposer in life.
Symptoms of ADHD in Children
It’s important to keep in mind that it is typical for many children to showcase similiar symptoms of ADHD. However, children diagnosed with ADHD have symptoms that are much more frequent and severe, and can heavily interfere with daily life. Here is a list of the main symptoms of ADHD:
Inattention:
- Problems with paying attention to details or making careless mistakes during homework.
- Trouble staying focused on tasks or play activities.
- Frequently losing train of thought or becoming easily distracted.
- Difficulty following through with instructions or finishing tasks.
Hyperactivity:
- Fidgeting and squirming while seated.
- High energy levels when expected to remain seated.
- Climbing on furniture, walls, or other inappropriate places.
- Being unable to play quietly or relax calmly.
- Always “on the go” Impulsivity.
- Blurting out answers to questions before the speaker has finished.
- Difficulty waiting one’s turn in games or group situations.
Frequently interrupting conversations between others or intruding on their activities.
Types of ADHD in Children
There are three types of ADHD, each categorized depending on the symptoms that appear most:
- Predominantly Inattentive Presentation: Previously referred to as ADD, this kind of ADHD is characterized by a child’s difficulty in paying attention and staying focused. These children often seem withdrawn or lost in their thoughts, which frequently goes unnoticed.
- Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation: This type presents itself through excessive amounts of hyperactivity and impulsivity in children who suffer from it; they may be constantly moving around, unable to sit still, and fidgety all the time – leading them to struggle with self-control, resulting into disruptive behaviors.
- Combined Presentation: This type is known as the most common among others where kids have symptoms related to inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity.
Diagnosing ADHD in Children
Typically, diagnosing ADHD symptoms in children is done using a full assessment by any qualified medical professional, such as a pediatrician or child psychiatrist. The assessment may include:
- Comprehensive medical history and current symptom evaluation
- Reports from parents and teachers on the child’s behavior at home and school
- Psychological tests to measure cognitive abilities and eliminate other disorders.
ADHD cannot be diagnosed with one test alone; several factors must be considered. Early identification of this condition can help kids acquire treatment and thus provide necessary support.
Treatment Options for ADHD in Children
Managing ADHD effectively usually requires a mix of behavior-based strategies, educational support, and sometimes medication. Here are the main treatment methods for kids with ADHD:
- Behavioral Therapy: Parent training programs, classroom management techniques, and social skills training can help children learn coping mechanisms and improve their self-control.
- Educational Support: Individualized education plans (IEPs) or a 504 plan can offer accommodations and modifications to aid academic success. This could mean extended time on assignments, preferential seating, or breaks during tasks.
- Medicine: In general, stimulant medications are drugs like Adderall or Ritalin (amphetamine-based or methylphenidate) that are prescribed for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. These drugs help to control brain neurotransmitter levels, which increases impulse control, focus and attentiveness. Strattera is a non-stimulant drug that may be recommended in children who do not respond well to other treatments or have concerns about side effects.
- Support from Parents: Parental support is crucial when dealing with children diagnosed with ADHD. Learning good parenting skills, setting up regular routines and giving constant praise and rewards can all help to combat behavioral issues
However, it should be remembered that treatment ought to be tailored to each child’s individual needs and preferences.
Living with ADHD in Children: Tips for Parents and Caregivers
Caring for a child who has ADHD may be tough, but they can still thrive when the right systems and strategies are in place. Below are some tips to help them out:
- Learn About It: Understanding ADHD will let you know what to expect and how best to respond.
- Communicate: Have thorough conversations with your child about their ADHD diagnosis.
- Routine Building: Create regular mealtimes, bedtimes, homework times, etc. This can provide children with predictability and structure.
- Focus On The Good: Concentrate on praising good behavior and effort more than pointing out mistakes.
- Be Organized: Divide tasks into smaller parts that are easy to manage and use visual aids such as charts or lists.
- Find Help: Join support groups where parents or caregivers share experiences and offer each other resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can children grow out of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?
ADHD is chronic and typically carries into adolescence and adulthood. However, symptoms may evolve and improve with age-, most often in the case of hyperactivity. Most children learn to adapt as they mature if provided with proper treatment and support systems.
What happens when ADHD is not treated for a long time?
Untreated ADHD can lead to problems at school and in relationships. Kids with ADHD may also have low self-esteem, troubled emotions, or poor performance in school. Adults with untreated ADHD may have trouble finding jobs or staying employed, problems with relationships, and difficulty managing their finances. They may also have additional mental health disorders, such as depression or anxiety.
Also Read:
Contact Us Today
Book an in-person or online visit in seconds. Call (312) 971-7147 or click on Book Appointment.